Most cases of chlamydia trachomatis occur in young women, however it can affect people of any age and in both sexes. Although treatable, it might cause more significant health issues if left untreated.
Read also: Men, here is how to tell if you have STDs
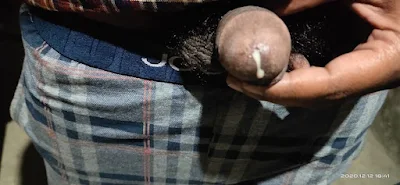
Chlamydia trachomatis infection causes painiful urination in men and whitish discharge that occurs in both women and men. Complications of this disease include pelvic innflamatory disese and swelling of ball testicles in men. Chlamydia can occur on different body parts anal region, on the tounge and vagina and the penis depending on what kind of sex they practice.
Symptoms
Symptoms of this diseaase may not appear or they delay especially in women because of the target part. In men however the symptoms shows within 5 days on getting it.
Symptoms of chlamydia if they occur include:
- Whitish light discharge from your penis
- Pain when passing urine
- Abnormal vaginal discharge
- Bleeding that is not due to menses or after sex
- Painful and swollen testicles
- Women feel pain during sexual activity
Transmission
What are the Risks factors?
- Reduced use of condoms.
- Reduced usage of medical services for STD treatment and prevention.
- Several sexual partners.
- Switching partners before discovering one has a chlamydia infection.
Complications
One may relate Chlamydia trachomatis with:
- Prostatitis (Infection of the prostate gland). The chlamydia bacteria sporadically spreads to the prostate gland. Lower back pain, fever, chills, painful urination, and pain during or after intercourse are all possible symptoms of prostatitis.
- Neonatal infection. During childbirth, a chlamydia infection can spread from the vaginal canal to the newborn, perhaps leading to pneumonia or a dangerous eye infection.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). Pelvic pain and fever are symptoms of PID, an infection of the uterus and fallopian tubes. Hospitalization may be necessary for intravenous antibiotics in cases of severe illnesses. PID can harm the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and cervix.
- Epididymitis. an infection close to the testicles. The epididymis, a coiled tube that lies next to each testicle, can become inflamed due to a chlamydia infection. Infections may cause scrotal discomfort, edema, and fever.
- Ectopic pregnancy. This happens, generally in a fallopian tube, when a fertilized egg implants and grows outside the uterus. It is necessary to terminate the pregnancy in order to avoid potentially fatal consequences like a burst tube. An infection with chlamydia raises this risk.
- Unable to conceive (Infertility). Even infections with no symptoms or signs of chlamydia can lead to fallopian tube blockage and scarring, which can render women infertile.
- Swollen joints (Reactive Arthritis). Individuals with Chlamydia trachomatis are more likely to experience Reiter syndrome, which is another name for reactive arthritis. Usually, this illness affects the urethra, which is the tube that travels from your bladder to the outside of your body, as well as the joints and eyes.
Prevention
Here are the ways you can use:
- Use condoms consistently. During every sexual encounter, wear a female polyurethane condom or a male latex condom. When used correctly, condoms lessen but do not completely eliminate the risk of infection during every sexual contact.
- Don't have too many sexual partners. You run a greater chance of catching chlamydia and other STDs if you have several sexual partners.
- Get screed for STIs regularly. See your physician about the frequency of chlamydia and other STD screenings if you engage in sexual activity, especially if you have several partners.
- Avoid douching. Douching can raise the risk of infection because it reduces the amount of beneficial bacteria in the vagina.
- Get treated with your partner. This will ofcourse prevent getting infection again from the same person if they awere not treated together with you.